
Neurological Organoids and Space Farming
-
by Anoop Singh
- 8

The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on November 8, 2021. Credit: NASA
Astronauts on Expedition 71 will explore neurological, botanical, and physiological responses to space, contributing to safer space travel and sustainable life support systems.
Studies of neurological organoids, plant growth, and shifts in body fluids are among the scientific investigations that NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, Jeanette Epps, and Tracy C. Dyson will help support aboard the International Space Station as part of Expedition 71. Barratt joins a group of astronauts participating in a suite of experiments, Complement of Integrated Protocols for Human Exploration Research or CIPHER, that is helping scientists learn how extended durations in space change the human body. The crew launched on March 3 and will dock to the station on March 5.
Here are details on some of the work scheduled during this upcoming expedition aboard the microgravity laboratory:
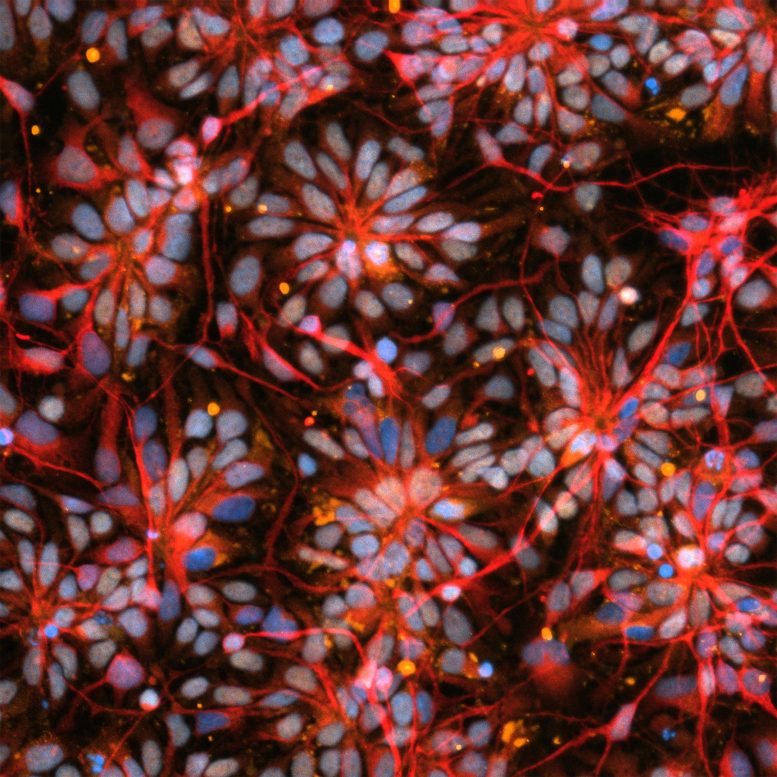
Brain organoid cells from the previous investigation Cosmic Brain Organoids are made of cells from people with Parkinson’s Disease and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Credit: New York Stem Cell Research Institute
Modeling Neuroinflammation
Human Brain Organoid Models for Neurodegenerative Disease & Drug Discovery (HBOND) studies the mechanisms behind neuroinflammation, a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders.
Researchers create organoids using patient-derived iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells) from patients who have Parkinson’s disease and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. The sixth space station organoid investigation funded by the National Stem Cell Foundation, HBOND includes for the first time Alzheimer’s iPSCs and testing of the effects of drugs in development to treat neuroinflammation.
Results could help improve diagnostics, provide insights into the effects of aging, accelerate drug discovery, and identify therapeutic targets for patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases. The organoid models also could provide a way to anticipate how extended spaceflight affects the brain and support development of countermeasures.
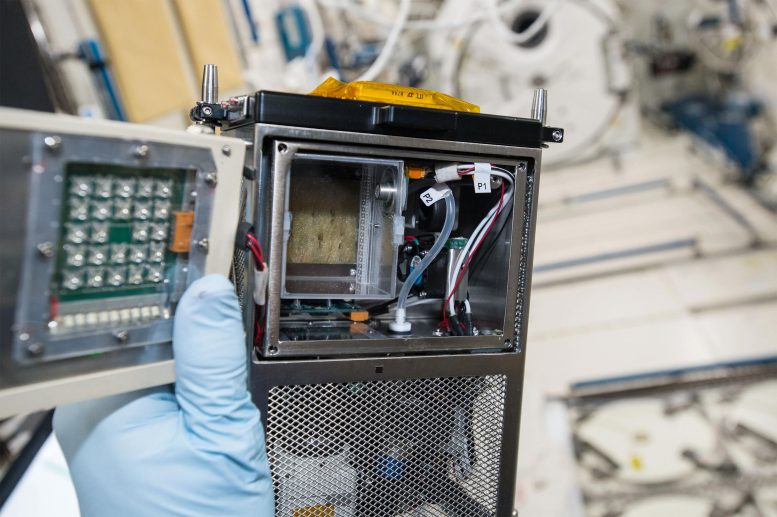
This image shows the Plant Experiment Unit (PEU) hardware for the Plant UV-B investigation. Credit: NASA
Protecting Plants From Spaceflight Stressors
Plants can serve as a source of food and provide other life-support services on long-term missions to the Moon and Mars. The Study on Plant Responses Against the Stresses of Microgravity and High Ultraviolet Radiation in Space (Plant UV-B) examines how stress from microgravity, UV radiation, and the combination of the two affect plants at the molecular, cellular, and whole organism levels. Results could increase understanding of plant growth in space and support improvements in plant cultivation technologies for future missions.
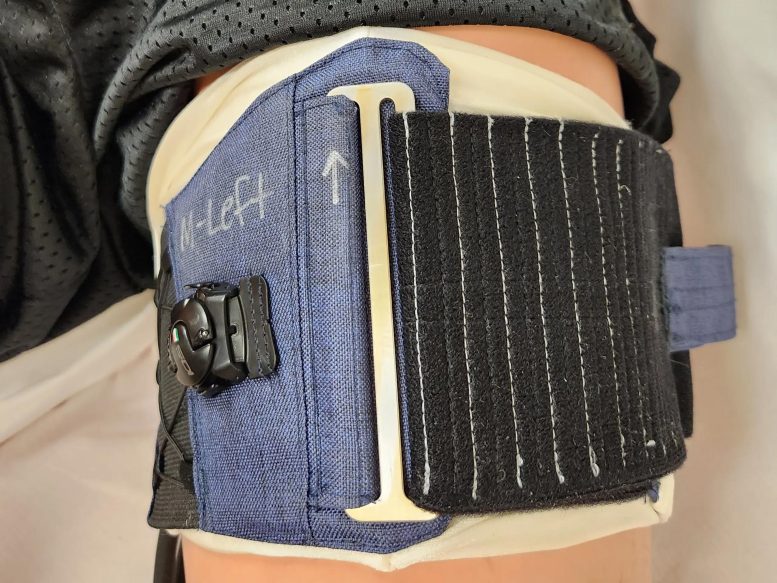
A test subject wears the device for the Thigh Cuff investigation pre-flight. Credit: NASA
Reversing Fluid Shifts
Weightlessness causes fluids in the body to move toward the head, which can cause changes in eye structure and vision known as Spaceflight Associated Neuro-ocular Syndrome (SANS) along with other health problems. Mitigating Headward Fluid Shifts with Veno-constrictive Thigh Cuffs During Spaceflight (Thigh Cuff) examines whether thigh pressure cuffs could provide a simple way to counter this shift in body fluids and help protect astronauts from SANS and other issues on future missions to the Moon and Mars.
Thigh cuffs also could help treat or prevent problems for patients on Earth who have conditions that cause fluid accumulation in the head, such as long-term bed rest and diseases.
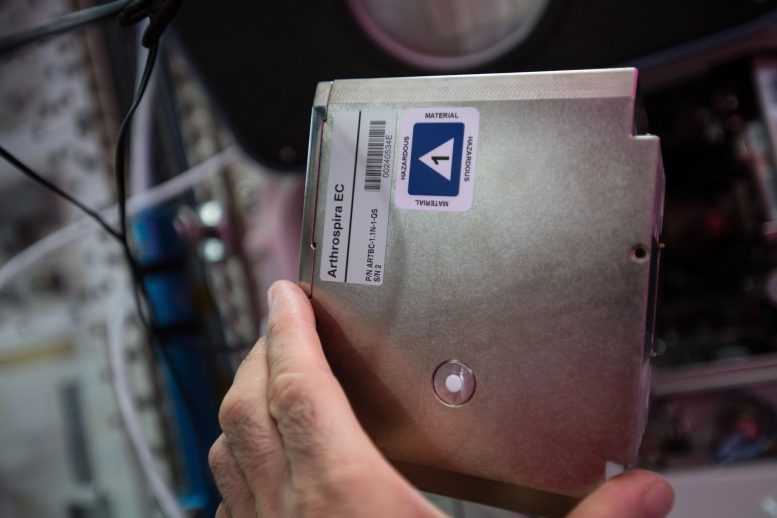

The container on the space station for Arthrospira-B, an investigation previous to Art-C. Credit: NASA
Incredible Edible Algae
Arthrospira-C (Art-C), an investigation from ESA (European Space Agency) analyzes how the cyanobacterium Limnospira responds to spaceflight conditions and whether it produces the same quantity and quality of oxygen and biomass in space as on Earth. These microalgae, also known as Spirulina, could be used to remove carbon dioxide exhaled by astronauts, which can become toxic in an enclosed spacecraft, and to produce oxygen and fresh food as part of life support systems on future missions.
Correct predictions of oxygen and biomass yields are crucial for design of life support systems using bioprocesses. Spirulina also has been shown to have radioprotective properties and eating it could help protect space travelers from cosmic radiation, as well as conserve healthy tissue in patients undergoing radiation treatment on Earth.
The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on November 8, 2021. Credit: NASA Astronauts on Expedition 71 will explore neurological, botanical, and physiological responses to space, contributing to safer space…
The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on November 8, 2021. Credit: NASA Astronauts on Expedition 71 will explore neurological, botanical, and physiological responses to space, contributing to safer space…
