
Intel 12th Gen P series vs U series: which one to choose and why
-
by Anoop Singh
- 8
Intel’s 12th Gen Alder lake processors bring the most significant shift in its X86 architecture. Alder Lake CPUs follow a new performance hybrid architecture and employ two types of cores – Performance (P-core) and Efficient (E-cores). The P-cores handle high-performance cores for compute-intensive workloads and the E-cores consume very little power and can handle background tasks or delivers multithreaded performance for tasks that run in parallel.
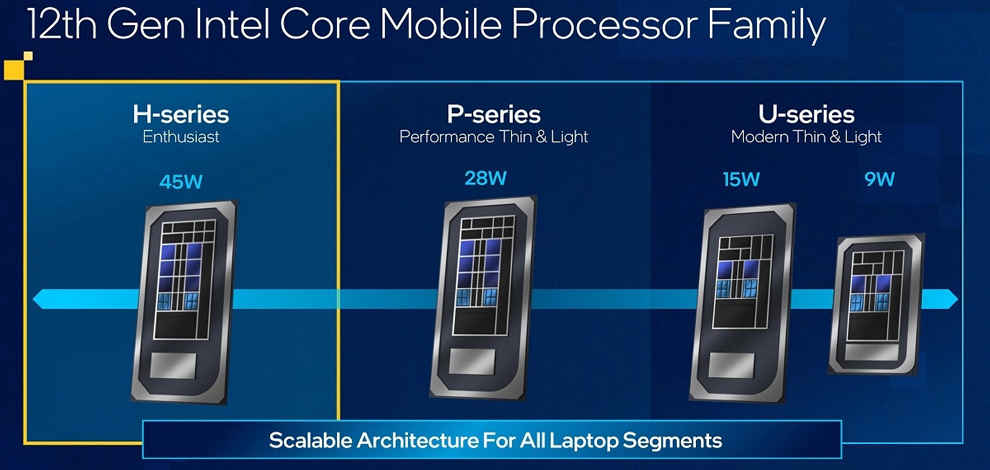
With the new hybrid design, Intel has also changed its processor classification. Till the 11th generation, ultra-portable thin and light laptops were usually addressed with the U-series. New thin and light laptops, however, will come in the P and U series, denoted by the P and U suffix at the end ( For instance, Core i7-1280P or i7-1265U).
Apart from the P and U series, there is also the H series which includes 45W offerings meant for gaming workloads and creator workstations.
The P and U series options are meant for thin and light laptops, and if you have been looking to buy one, it’s understandable that you are confused between the two. Let’s walk you through the details so you can make an informed choice.

Intel U Series
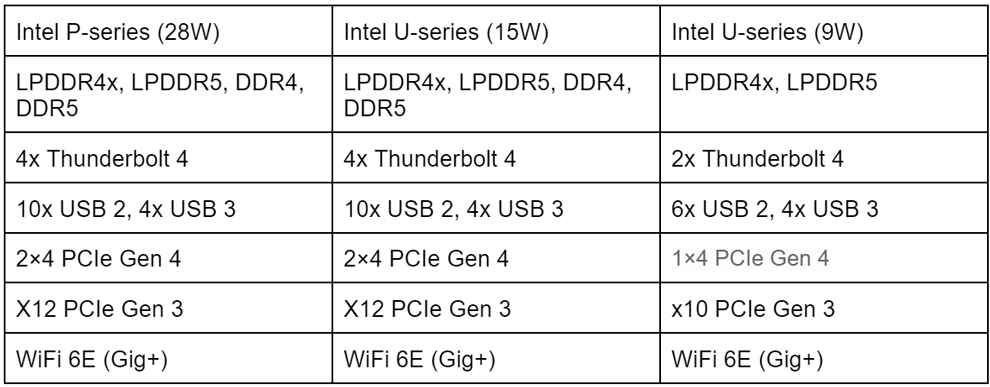
Intel U series processors come in two power configurations – 9W and 15W. 9W chips are extremely power-efficient and are being used in ultra-portable thin and light laptops with awesome battery life. The 15W U-series is the most popular among 12th gen Intel core thin and light laptops. It is better suited for portable options that occasionally need to run demanding applications.
Here’s how you can differentiate between the two – the model number of all 9W U series chips end in 0U or a 0 before the U suffix. All 15W chips, on the other hand, end in a 5U or a 5 before the U suffix at the end. So a Core i7-1265U is a 15W chip, while a Core i7-1260U is a 9W chip.
The 15W designs have a bigger package (UP3) as compared to the 9W options (UP4), but the layout essentially remains the same. The number of cores remains exactly the same across comparable SKUs.
With both the 9W and 15W chips, you get up to 2 P-cores, up to 8 E-cores and up to 96 execution units of graphics.


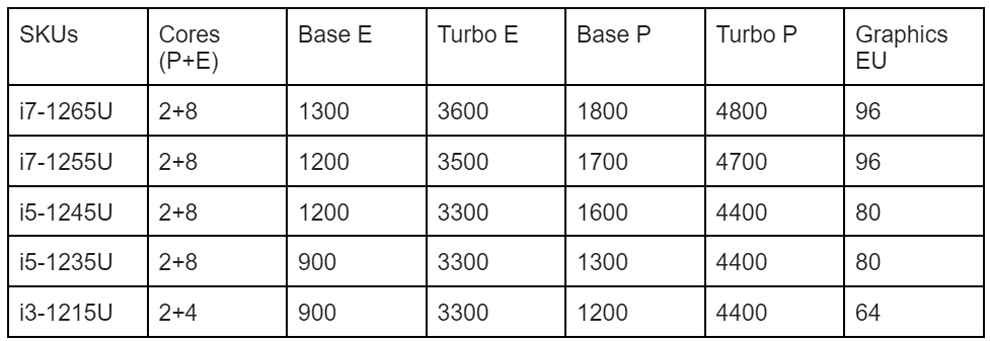
Intel Core 15W U Series CPUs

Intel Core 9W U Series CPUs
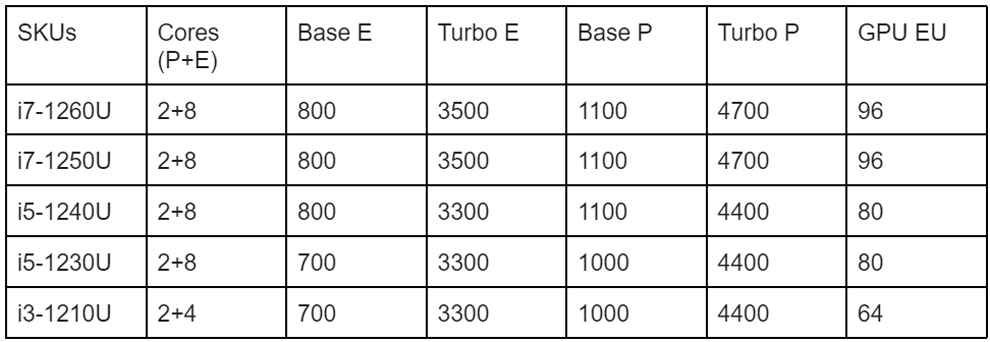

As you’d expect, the 9W U-series chips have lower base frequencies for both CPU and GPU cores as compared to the 15W options. The turbo frequencies and L3 cache remain similar.
The 9W chips only have support for Low power LPDDR4-4267 and LPDDR5-5200. The 15W chips additionally support DDR4-3200 and DDR5-4800, which implies that manufacturers can add double the maximum RAM capacity. This, however, won’t make much of a difference in practical scenarios.
Intel P Series


Intel P series processors consume a lot more power (28W base, 64W turbo) and deliver a lot more performance. These processors are meant for thin and light laptops that need to frequently handle demanding software.
The P series processors have up to 6 performance cores, 8 performance cores, up to 96 GPU execution units, and a bigger L3 cache compared to U series chips. There are 6P series processors in total and you can identify them with the P suffix at the end.
Intel Core 28W P Series CPUs
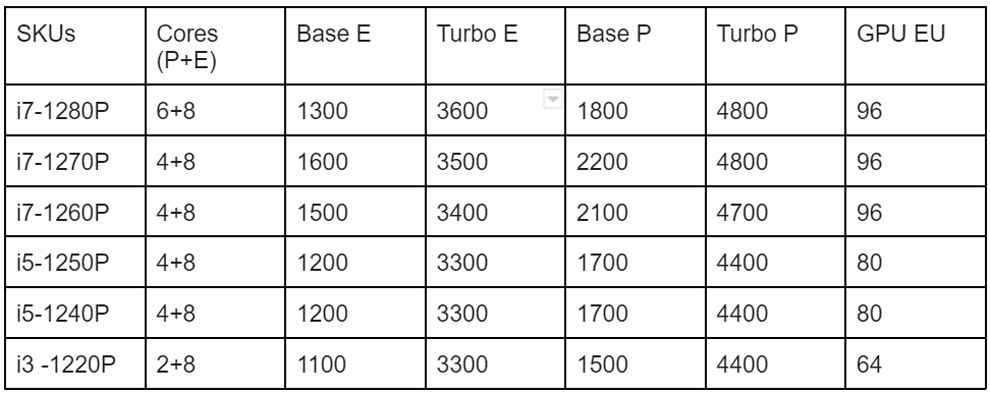

The P series processors support also have Turbo Boost Max 3.0. It means that one of the Performance cores can attain a higher turbo frequency to boost performance.
To sum it up
All of these 12th gen processors offer great performance. These processors are now part of the Intel Evo specs and are being employed in several popular Intel Evo-certified laptops. This indeed makes the platform very promising and should help take the performance and power efficiency of thin and light laptops to the next level.
The Intel P-series and 15W U-series chips have many similarities since they are both based on the same package. If you prioritize battery life and ultra-portable form factor, the 9W U-series chips will serve you well. They are mostly being used on foldable and slim convertibles like Asus Zenbook 17 Fold OLED.
If you expect your thin and light laptop to do some occasional heavy-lifting, the 15W U-series chips will offer a great balance between performance and battery life. These include options like HP Spectre x360, Galaxy Book2 and Dell Inspiron 7420.
And if running demanding applications is a primary use case, you can consider laptops like Galaxy Book2 Pro and ASUS Vivobook 15 (2022) that employ P-series Processors and are also Intel Evo certified.

[Sponsored]
Intel’s 12th Gen Alder lake processors bring the most significant shift in its X86 architecture. Alder Lake CPUs follow a new performance hybrid architecture and employ two types of cores – Performance (P-core) and Efficient (E-cores). The P-cores handle high-performance cores for compute-intensive workloads and the E-cores consume very little power and can handle background…
Intel’s 12th Gen Alder lake processors bring the most significant shift in its X86 architecture. Alder Lake CPUs follow a new performance hybrid architecture and employ two types of cores – Performance (P-core) and Efficient (E-cores). The P-cores handle high-performance cores for compute-intensive workloads and the E-cores consume very little power and can handle background…
